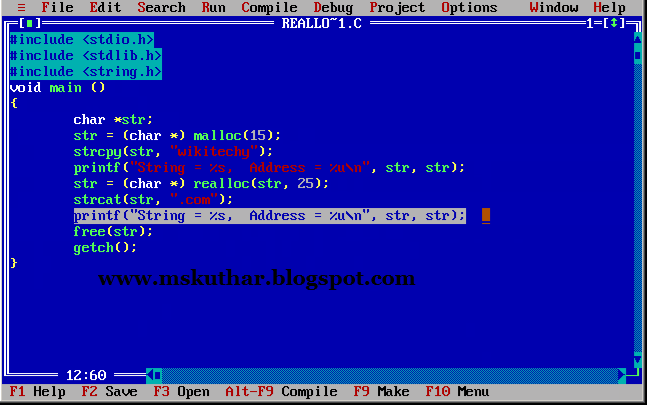
realloc() function in C
- When memory is not available for malloc) (or calloc), (the memory can be re-allocated by the function reloc). (For short, it does change the size of the memory.
- Let's see the syntax of realloc() function.
ptr=realloc(ptr, new-size)
free() function in C
- The memory occupied by malloc() or calloc() functions must be released by calling free() function. Otherwise, it will consume memory until program exit.
- Let's see the syntax of free() function.
- free(ptr)
 |
| Use of free() |
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int *ptr, i , n1, n2;
printf("Enter size: ");
scanf("%d", &n1);
ptr = (int*) malloc(n1 * sizeof(int));
printf("Addresses of previously allocated memory: ");
for(i = 0; i < n1; ++i)
printf("%u\n",ptr + i);
printf("\nEnter the new size: ");
scanf("%d", &n2);
// rellocating the memory
ptr = realloc(ptr, n2 * sizeof(int));
printf("Addresses of newly allocated memory: ");
for(i = 0; i < n2; ++i)
printf("%u\n", ptr + i);
free(ptr);
return 0;
}
Output will be
Enter size: 2
Addresses of previously allocated memory:26855472
26855476
Enter the new size: 4
Addresses of newly allocated memory:26855472
26855476
26855480
26855484
Tags:
c by mskuthar
C Programming Language
free() functions
mskuthar
realloc()
www.mskuthar.blogspot.com
