Switch statement
- The if and if-else statements permit two way branching whereas switch statement permits multiple branching. The syntax of switch statement is:
{
case constant1 :
statement 1;
break;
case constant2 :
statement2;
break;
.
.
default: statement3;
break;
}
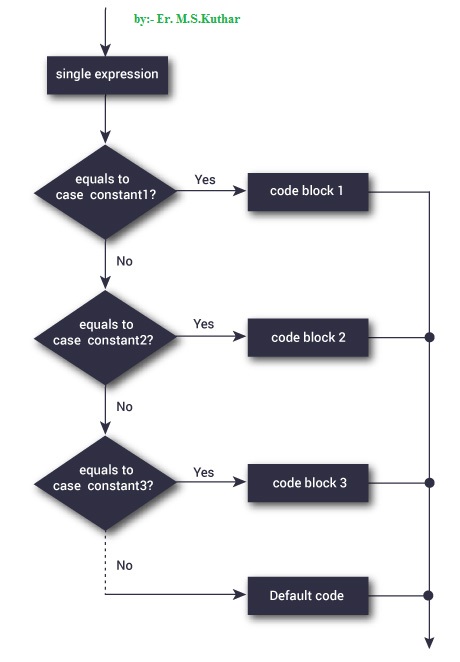
- The execution of switch statement begins with the evaluation of expression.
- If the value of expression matches with the constant then the statements following this statement execute sequentially till it executes break.
- The break statement transfers control to the end of the switch statement.
- If the value of expression does not match with any constant, the statement with default is executed.
Flowchart of Switch Statement is given below.
 |
| Switch Statement |
Some important points about switch statement
- The expression of switch statement must be of type integer or character type.
- The default case need not to be used at last case. It can be placed at any place.
- The case values need not to be in specific order.
For Example:
#include <iostream.h>
int main ()
{
// local variable declaration:
char grade = 'C';
switch(grade)
{
case 'A' :
cout << "A grade" << endl;
break;
case 'B' :
cout << "B grade" << endl;
break;
case 'C' :
cout << "C grade" << endl;
break;
case 'D' :
cout << "D grade" << endl;
break;
case 'F' :
cout << "E grade" << endl;
break;
default :
cout << "Invalid grade" << endl;
}
cout << "Your grade is " << grade << endl;
return 0;
}
Output :
C grade
Your grade is C
/* Source code to create a simple calculator for addition, subtraction, multiplication and division using switch...case statement in C++ programming. */
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char o;
float num1,num2;
cout << "Enter operator either + or - or * or /: ";
cin >> o;
cout << "Enter two operands: ";
cin >> num1 >> num2;
switch(o) {
case '+':
cout << num1+num2;
break;
case '-':
cout << num1-num2;
break;
case '*':
cout << num1*num2;
break;
case '/':
cout << num1/num2;
break;
default:
/* If operator is other than +, -, * or /, error message is shown */
cout << "Error! operator is not correct";
break;
}
return 0;
}
Output
Enter operator either + or - or * or divide : -
Enter two operands:
3.4
8.4
3.4 - 8.4 = -5.0
Tags:
C programming
c switch statement
cpp prigramming
mskuthar
Switch statement in C++.
Switch statement.
