C Pointer to Pointer
- In C pointer to pointer concept, a pointer refers to the address of another pointer.
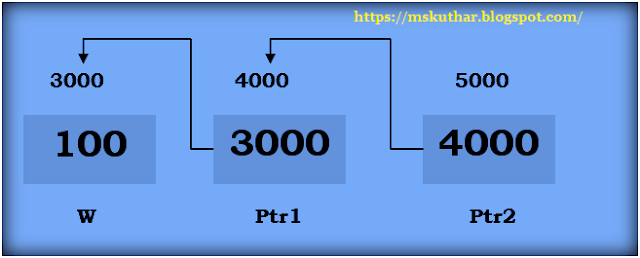
- In c language, a pointer can point to the address of another pointer which points to the address of a value. Let's understand it by the diagram given below:
 |
| Pointer to Pointer |
- Let's see the syntax of pointer to pointer.
int **p2;
C pointer to pointer example
- Let's see an example where one pointer points to the address of another pointer.
- As you can see in the above figure, p2 contains the address of p (fff2) and p contains the address of number variable (fff4).
Changing Value Pointed by Pointers
Let's take an example.
int* pc, c;
c = 5;
pc = &c;
c = 1;
printf("%d", c); // Output: 1
printf("%d", *pc); // Ouptut: 1
- We have assigned the address of c to the pc pointer.
- Then, we changed the value of c to 1. Since pc and the address of c is the same, *pc gives us 1.
#include <conio.h>
void main(){
int number=50;
int *p;//pointer to int
int **p2;//pointer to pointer
clrscr();
p=&number;//stores the address of number variable
p2=&p;
printf("Address of number variable is %x \n",&number);
printf("Address of p variable is %x \n",p);
printf("Value of *p variable is %d \n",*p);
printf("Address of p2 variable is %x \n",p2);
printf("Value of **p2 variable is %d \n",**p);
getch();
}
Expected Output:-
Address of number variable is fff4
Address of p variable is fff4
Value of *p variable is 50
Address of p2 variable is fff2
Value of **p variable is 50